Overview
Schema markup, or ‘structured data’, is one of the most powerful and underutilized forms of web content optimization. It can help you to jump ahead of your competitors’ right to the top of the SERPs and control how your content appears on the results pages.
But despite how powerful structured data can be, many marketers and SEOs still don’t even know what it is. In this article, we’ll be introducing you to the basics of structured data and showing you how to implement it on your own website pages.
What is Schema?
In a nutshell, a schema tells search engines like Google what the content on your website means.
It helps search engines to understand what’s on the page by organizing and interpreting the information on there. You can think of it kind of like a ‘labeling’ system that helps to classify the page content.
It’s probably easier to understand through an example, so let’s look at one. Take a look at how this recipe page appears on the SERPs – notice anything interesting?
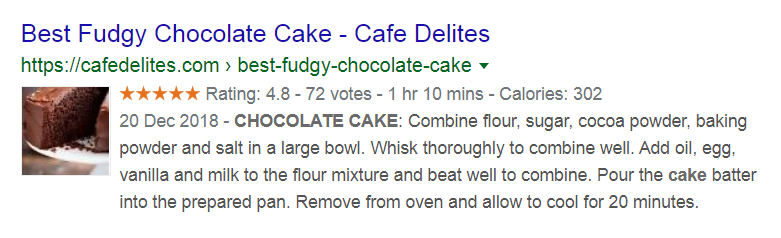
Aside from the usual URL, title, and meta description, there are a few extra elements to this result that are only there because of structured data: the rating, the vote count, the cooking time, and the calorie information.

“Google was able to pick out all that information and display it correctly because a schema markup had ‘labeled’ these different elements to tell Google what they meant, and how to present them in the SERPs.”
Michael Jenkins
The recipe page example comes up a lot because it offers an excellent illustration of how schema can be used, but there are many other examples. For example, it could be used to label different events alongside their dates on event listing pages.
Why it matters for SEO
Surprisingly, schema doesn’t actually influence website rankings – but that doesn’t mean it’s not important for SEO.
It does something arguably even more important: it influences the ‘rich results’. Rich results are elements that appear in position 0 in the search engine results pages, right at the top, like in the example below.
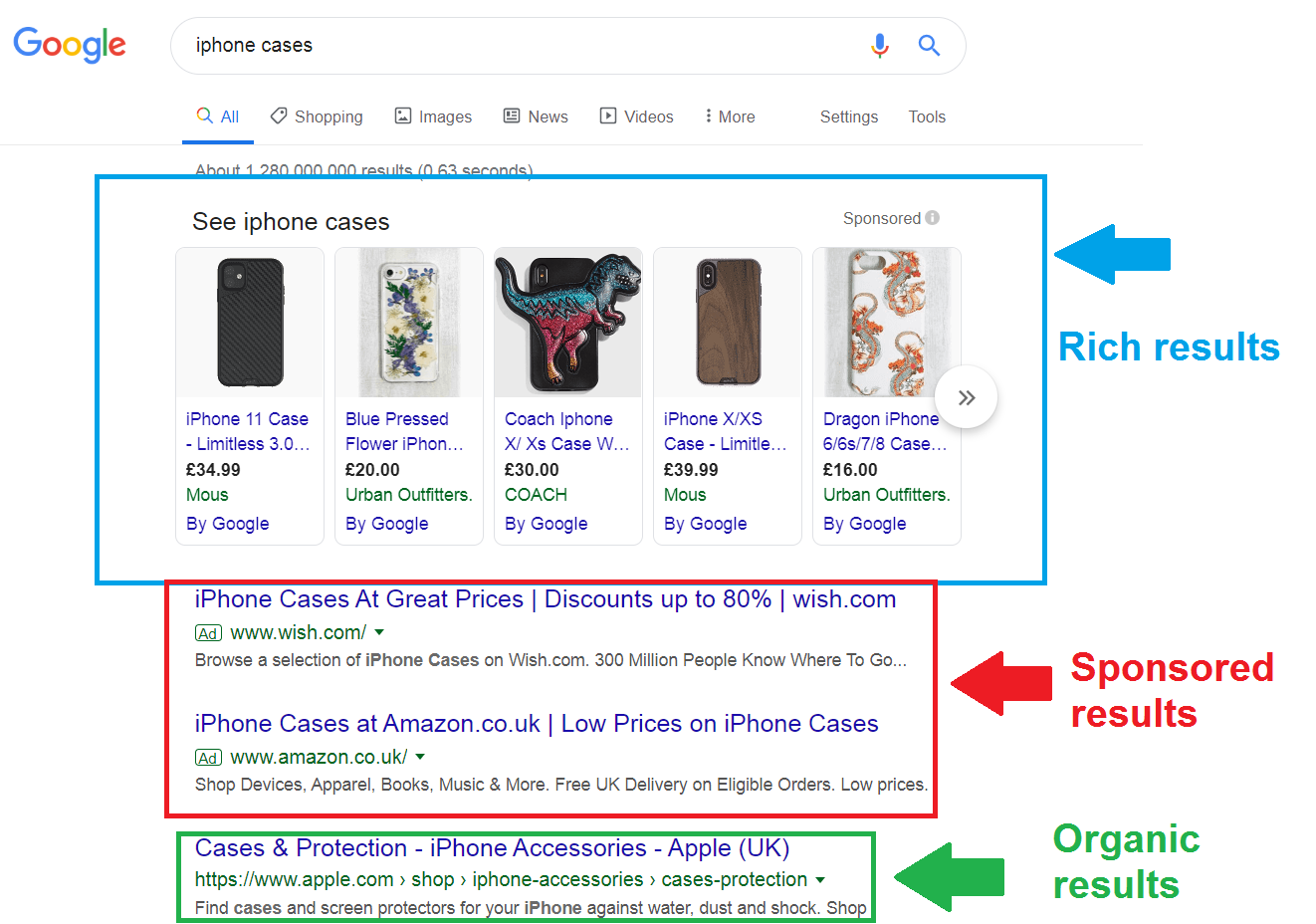
Google pulls information out of websites and showcases them in these rich results when relevant. But to do this, it has to understand what the information on your website means first, which is where schema comes in.
By marking up the content properties of your pages, you make them eligible for inclusion in rich results. These rich results are especially important for local SEO as it can help local businesses to get their contact number, opening hours, and address listed in the Knowledge Panel for their brand terms.
Structured data can also help to boost your SEO and improve your rankings indirectly. Marking up your content makes your page look more attractive in the search results pages. Organized data means that users can see more about the content of your webpage at a glance before they click it, and this can improve your clickthrough rates and dwell time.
And while structured data might not be a ranking factor, clickthrough rates and dwell time certainly are.
How does it work?
Structured data is built on HTML code, which Google reads to understand the content on your website.
To add structured data, all you have to do is create these snippets of code and add them to your content management system.
Of course, most of us don’t have a whole lot of HTML coding knowledge but, fortunately, we don’t need to. Google, Bing, and Yahoo have collaborated to create a free tool that makes marking up your data easy for all users, Schema.org.
All you have to do is the following:
- Visit schema.org
- Select the type of content you want to markup
- Paste in the content page URL and click ‘start tagging’
- Highlight the text you want to markup (or ‘label’) in the interface, then click the tag you want to add. For example, you can highlight the author’s name and click ‘author’. Keep adding markup items until you’re finished
- Click ‘create HTML’
- Copy and paste the HTML code into your CMS post/page source code
That’s all there is to it.
3 Important SCHEMA implementations
As you might have noticed, there are lots of different elements you can markup. It’s not necessary to mark up everything for every kind of post (you’d be at it all day if you tried) but here are some of the more important schema implementations you might want to include.
1. Products
The product structured data snippet is really useful, especially for eCommerce sites. You can use it to highlight specific products in the SERPs and share extra information about them, including things like pricing and reviews.
2. FAQs
The FAQ structured data snippet pulls out the answers to frequently asked questions from your content and lists them underneath your page description, like in the example below.
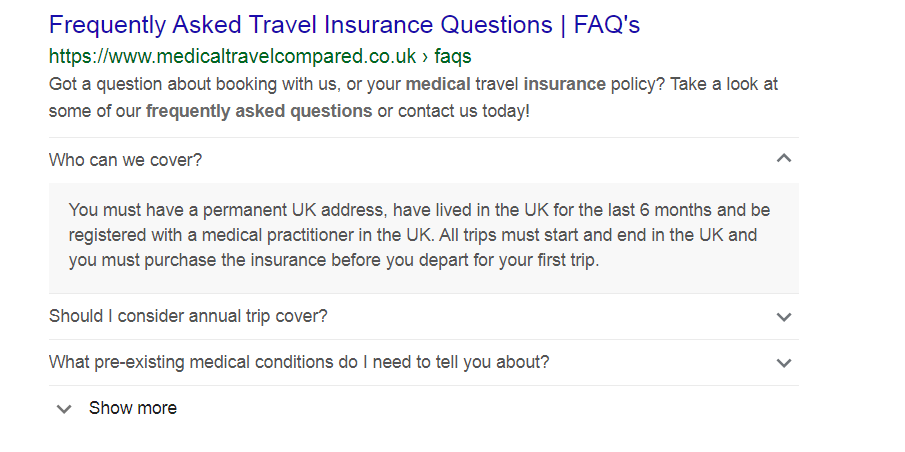
This can be really helpful both for providing a great user experience and for dominating more space in the SERPs.
3. Corporate contact
Another important schema implementation is the ‘corporate contact’ structured data snippet. This helps search engines to pull out important information about your company, including your contact details, social media profiles, and more. It’s very important for local businesses.